La enfermedad del hígado graso es una afección prevalente que afecta a muchas personas en todo el mundo. Uno de los principales contribuyentes a esta enfermedad es la obesidad. En el mundo acelerado de hoy, los hábitos alimenticios a menudo no son saludables, lo que lleva a un desequilibrio en el cuerpo y numerosos problemas de salud.
Tipos de enfermedad del hígado graso
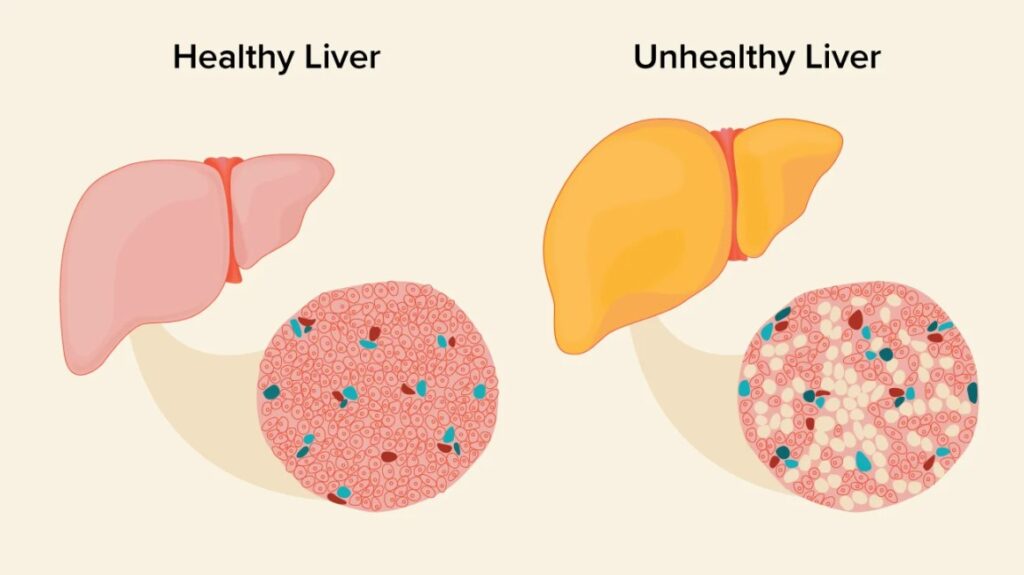
- Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD)
- Cause: Not related to excessive alcohol consumption.
- Effects: Causes inflammation and damage to liver cells.
- Progression: Does not typically worsen over time without additional contributing factors.
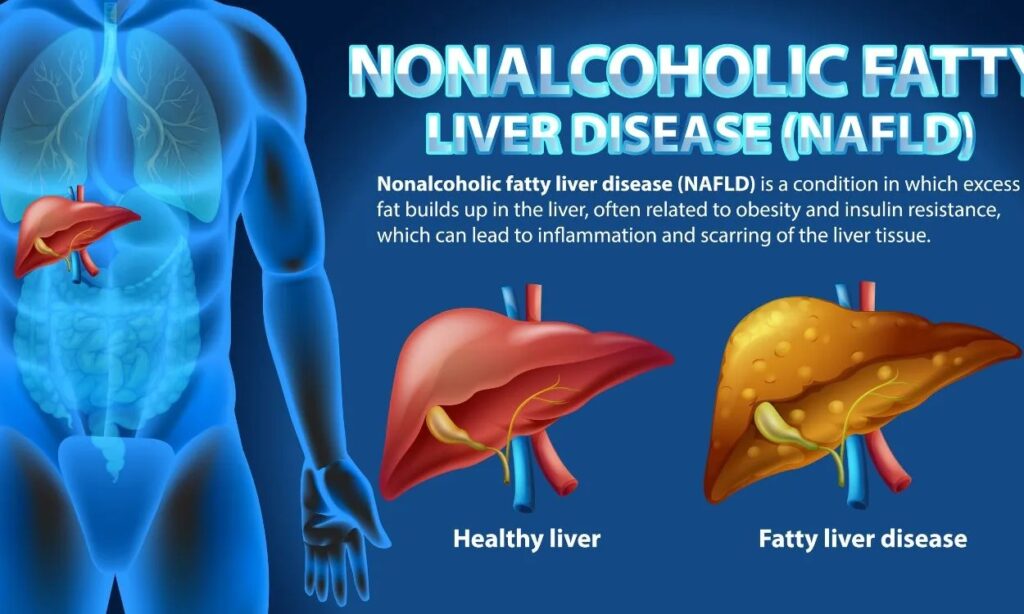
- Alcohol-Related Fatty Liver Disease (ARFLD)
- Cause: Directly related to excessive alcohol consumption.
- Effects: Can cause serious liver damage, including an enlarged liver.
- Symptoms: Early signs include pain and discomfort in the upper right side of the abdomen.
- Progression: Can improve with cessation of alcohol consumption; continued drinking can exacerbate the condition.
Síntomas y efectos en el cuerpo
- Abdomen
- Fluid Retention: Water retention in the abdomen, caused by pressure in the liver’s blood vessels due to inflammation, leading to swelling and pain.
- Foot
- Swelling: Persistent swelling in the feet can indicate liver disease, as fluid accumulates due to gravity. This swelling can also occur from normal activities, but when persistent, it should be checked by a healthcare provider.
- Legs and Ankles
- Swelling: The ankles, legs, and feet can swell due to liver disease. Enlarged veins put pressure on the kidneys, hindering their ability to filter and remove excess fluid from the body naturally.
- Chest
- Enlargement: Liver disease can cause enlargement of the chest walls due to hormonal imbalances. This condition can decrease sexual desire and increase the risk of infertility.

Comprender estos síntomas y sus posibles vínculos con la enfermedad hepática es crucial para la detección y el tratamiento tempranos. Los hábitos dietéticos adecuados y evitar el consumo excesivo de alcohol pueden reducir significativamente el riesgo de desarrollar la enfermedad del hígado graso.