Quick Summary

Consuming protein before bed can support muscle recovery and growth while you sleep. Research shows that 20-40 grams of slow-digesting protein 30-60 minutes before sleep may enhance overnight muscle protein synthesis, especially for athletes and active individuals.
Understanding Protein Timing
Your Daily Protein Needs
According to the Dietary Guidelines for Americans, your daily macronutrient intake should include:
- Protein: 10-35% of total calories
- Carbohydrates: 45-65% of total calories
- Fat: 20-35% of total calories
Standard recommendation: 0.8g of protein per kg of body weight For athletes and active individuals: 1.6-2.2g per kg of body weight
Quick Calculator:
- 180 lb (82 kg) active male: 130-180g protein per day
- 140 lb (64 kg) active female: 102-140g protein per day
Does Timing Matter?
The bottom line: Daily protein intake is most important, but timing can optimize results.
Research shows that distributing protein throughout the day—including before bed—may enhance muscle protein synthesis compared to consuming all your protein in fewer meals.
The Science: Why Protein Before Bed Works

What Happens While You Sleep
During sleep, your body enters an extended fasting state. Without protein intake, your body may break down muscle tissue to access amino acids. Here’s what protein before bed does:
1. Provides Amino Acids During Recovery
- Sleep is when muscle repair and growth occur
- Growth hormone peaks during deep sleep
- Protein supplies the building blocks needed for muscle synthesis
2. Increases Overnight Muscle Protein Synthesis
- Slow-digesting proteins release amino acids gradually
- Keeps your body in an anabolic (muscle-building) state
- Prevents muscle breakdown during the overnight fast
3. Supports Metabolic Health
- May increase resting metabolic rate
- Can improve next-morning metabolism
- Helps maintain lean muscle mass
Key Research Findings
Study 1: Acute Effects (Res et al., 2012)
- 16 healthy young men performed evening resistance training
- Group consuming 40g casein protein before bed showed significantly higher muscle protein synthesis rates overnight
- Published in Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise
Study 2: Long-term Training Adaptations (Snijders et al., 2015)
- 44 young men completed 12-week resistance training program
- Group consuming 27.5g protein + 15g carbs before bed showed:
- Greater increases in muscle strength
- Larger improvements in muscle size
- Enhanced muscle fiber growth
- Published in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition
Study 3: Older Adults (Kouw et al., 2017)
- Pre-sleep protein intake improved overnight muscle protein balance in elderly men
- Suggests benefits extend beyond young athletes
- Published in Journal of Nutrition
International Society of Sports Nutrition Position: “Casein protein (~30-40g) prior to sleep can acutely increase muscle protein synthesis and metabolic rate throughout the night” – particularly beneficial for athletes training early morning or evening.
Who Benefits Most From Pre-Sleep Protein?
✅ Strong Evidence for Benefits:
Athletes & Regular Exercisers
- Training 3+ times per week
- Resistance/strength training focus
- Endurance athletes with high training volumes
Early Morning Trainers
- Those who train fasted in the morning
- Need extended overnight amino acid availability
Evening Trainers
- Training after dinner
- Need recovery support during sleep
Older Adults (55+)
- Fighting age-related muscle loss (sarcopenia)
- Need enhanced protein synthesis support
⚠️ May Not Benefit:
Sedentary Individuals
- Limited evidence of benefit without regular exercise
- May increase morning insulin levels
- Could contribute to unwanted weight gain
Those with Specific Conditions
- GERD or acid reflux (may worsen symptoms)
- Kidney disease (consult doctor first)
- Difficulty sleeping after eating
What and How Much to Eat
Optimal Protein Amount
For most active individuals: 20-40 grams of protein
Why this range?
- 20g is sufficient to maximize muscle protein synthesis in most people
- 40g may provide additional benefits for larger individuals or intense training
- More than 40g doesn’t appear to provide extra benefits
Best Protein Sources Before Bed
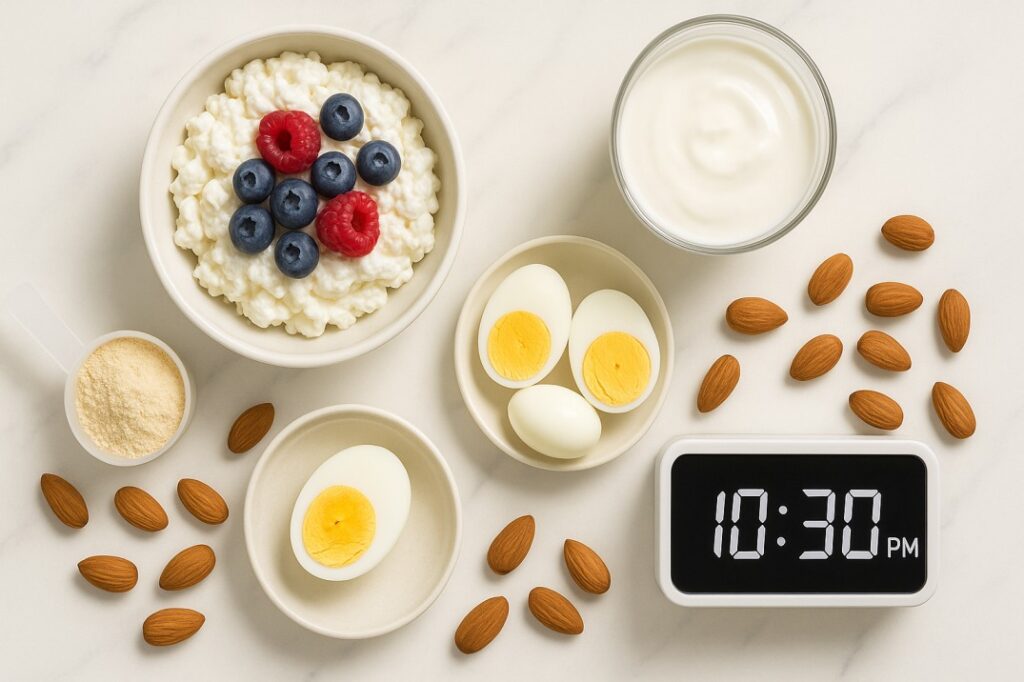

Slow-Digesting Proteins (Best Choice)
These digest gradually, providing sustained amino acid release:
Casein Protein (Gold Standard)
- Found naturally in dairy products
- Digests over 6-8 hours
- Sources: Cottage cheese, Greek yogurt, milk, casein protein powder
High-Protein Dairy Options:
- 1 cup cottage cheese (low-fat): ~25g protein
- 1 cup Greek yogurt (plain): ~20g protein
- 1 cup milk: ~8g protein
- Casein protein shake: 20-40g protein
Complete Protein Options
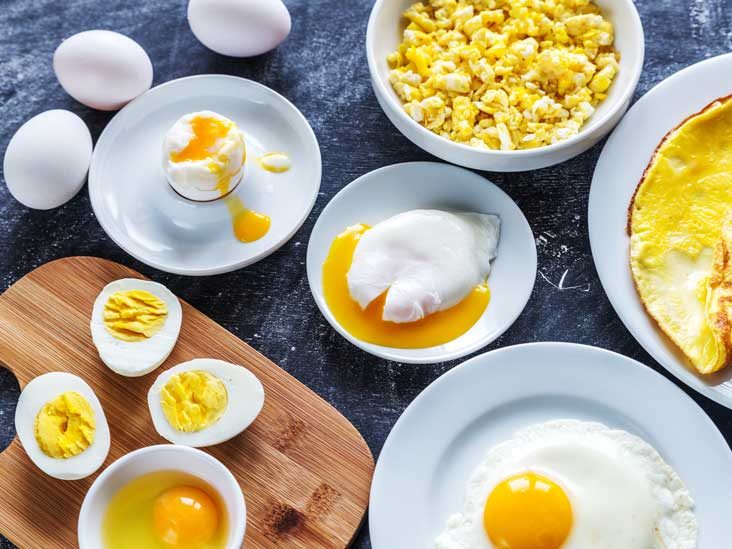
Animal Sources:
- 3 oz chicken breast: ~26g protein
- 3 oz turkey breast: ~25g protein
- 3 oz salmon: ~22g protein
- 3 hard-boiled eggs: ~18g protein
- 3 oz lean beef (90% lean): ~22g protein
Plant-Based Options:
- 1 cup cooked lentils: ~18g protein
- 1 cup edamame: ~17g protein
- 1 cup cooked chickpeas: ~15g protein
- Firm tofu (½ cup): ~20g protein
Easy Pre-Bed Snack Ideas

Option 1: Classic Cottage Cheese Bowl
- 1 cup low-fat cottage cheese
- Handful of berries
- Sprinkle of nuts or seeds → ~28g protein
Option 2: Greek Yogurt Parfait
- 1 cup plain Greek yogurt
- 1 tbsp almond butter
- Cinnamon → ~25g protein
Option 3: Protein Smoothie
- 1 scoop casein protein powder
- 1 cup unsweetened almond milk
- ½ banana
- Ice → ~25-30g protein
Option 4: Simple Turkey & Cheese
- 3 oz sliced turkey breast
- 1 oz cheese
- Whole grain crackers → ~28g protein
Option 5: Eggs & Toast
- 2-3 hard-boiled eggs
- 1 slice whole grain toast
- Avocado (optional) → ~18-22g protein
Protein Supplements vs. Whole Foods

When to Choose Whole Foods (Preferred)
Advantages: ✅ Complete nutrition (vitamins, minerals, fiber) ✅ More satiating ✅ No added sugars or artificial ingredients ✅ Better for overall health ✅ More affordable per serving
Best whole food choice: Low-fat cottage cheese or Greek yogurt
When Supplements Make Sense
Advantages: ✅ Convenience and portability ✅ Precise protein dosing ✅ Quick preparation ✅ Easier digestion for some people ✅ Useful if struggling to meet protein needs
Considerations: ⚠️ Less regulated by FDA ⚠️ May contain added sugars or artificial sweeteners ⚠️ Can be expensive ⚠️ Missing other nutrients from whole foods ⚠️ Some may contain contaminants
If using supplements: Look for third-party tested products (NSF Certified for Sport, Informed-Sport, or USP Verified)
Practical Implementation Guide
Timing Your Pre-Sleep Protein
Optimal window: 30-60 minutes before bed
Why this timing?
- Allows for initial digestion before lying down
- Reduces risk of digestive discomfort
- Provides amino acids throughout the night
Total Daily Protein Distribution
Ideal distribution pattern:
- Breakfast: 25-30g
- Lunch: 25-30g
- Dinner: 25-30g
- Pre-bed: 20-30g
Why distribute evenly? Research suggests spreading protein intake maximizes muscle protein synthesis better than consuming most protein in 1-2 large meals.
Tips for Success
1. Plan Ahead
- Prep snacks in advance
- Keep protein-rich options readily available
- Set a reminder 1 hour before usual bedtime
2. Monitor Your Response
- Track sleep quality
- Note any digestive issues
- Adjust timing or amount if needed
3. Stay Within Calorie Goals
- Account for pre-bed snack in daily totals
- Choose lean protein sources
- Watch added fats and sugars
4. Hydrate Appropriately
- Don’t overdrink right before bed
- Have small sips with your protein snack
Important Considerations & Warnings
Who Should Be Cautious
⚠️ Consult your doctor if you have:
- Kidney disease or impaired kidney function
- Diabetes (monitor blood sugar response)
- GERD or acid reflux
- Sleep disorders
Potential Downsides
For Sedentary Individuals:
- May increase morning insulin levels
- Could contribute to weight gain if calories exceed needs
- Benefits are minimal without regular exercise
General Cautions:
- Don’t exceed total daily calorie needs
- More protein isn’t always better (excessive intake can stress kidneys)
- Quality matters—choose nutrient-dense sources
Common Mistakes to Avoid
❌ Adding extra calories without adjusting daily intake ❌ Consuming too close to bedtime (causes discomfort) ❌ Choosing high-sugar protein bars or shakes ❌ Ignoring overall daily protein distribution ❌ Expecting results without adequate training stimulus
The Bottom Line for Athletes & Fitness Enthusiasts
Do’s ✅
- Consume 20-40g of protein 30-60 minutes before bed if you’re regularly active
- Prioritize slow-digesting proteins like casein, cottage cheese, or Greek yogurt
- Choose whole foods first, supplements when convenient
- Account for these calories in your daily total
- Be consistent for best results
- Combine with quality training and overall good nutrition
Don’ts ❌
- Don’t expect miracles without proper training
- Don’t exceed your total daily calorie needs
- Don’t rely solely on supplements
- Don’t eat immediately before lying down
- Don’t ignore sleep quality and recovery
- Don’t consume pre-bed protein if sedentary
Key Takeaway
Pre-sleep protein intake is a science-backed strategy for active individuals looking to optimize muscle recovery and growth. While total daily protein intake remains most important, consuming 20-40 grams of slow-digesting protein before bed can enhance overnight muscle protein synthesis.
This strategy works best when combined with:
- Regular resistance training (3+ times per week)
- Adequate overall protein intake (1.6-2.2g/kg body weight)
- Sufficient sleep (7-9 hours)
- Proper nutrition throughout the day
- Consistency over time
Remember: No single nutritional strategy replaces hard work, consistency, and a well-rounded approach to training and recovery.
Scientific References
- Res PT, Groen B, Pennings B, et al. (2012). “Protein ingestion before sleep improves postexercise overnight recovery.” Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise, 44(8):1560-1569.
- Snijders T, Res PT, Smeets JS, et al. (2015). “Protein ingestion before sleep increases muscle mass and strength gains during prolonged resistance-type exercise training in healthy young men.” The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 102(1):115-122.
- Trommelen J, van Loon LJ. (2016). “Pre-sleep protein ingestion to improve the skeletal muscle adaptive response to exercise training.” Nutrients, 8(12):763.
- Jäger R, Kerksick CM, Campbell BI, et al. (2017). “International Society of Sports Nutrition Position Stand: protein and exercise.” Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 14:20.
- Kouw IW, Holwerda AM, Trommelen J, et al. (2017). “Protein ingestion before sleep increases overnight muscle protein synthesis rates in healthy older men.” Journal of Nutrition, 147(12):2252-2261.
- Kinsey AW, Ormsbee MJ. (2015). “The health impact of nighttime eating: old and new perspectives.” Nutrients, 7(4):2648-2662.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and not intended as medical advice. Consult with healthcare professionals or registered dietitians before making significant dietary changes, especially if you have medical conditions or take medications.


