La stéatose hépatique est une affection répandue qui touche de nombreuses personnes dans le monde. L’obésité est l’un des principaux contributeurs à cette maladie. Dans le monde trépidant d’aujourd’hui, les habitudes alimentaires sont souvent malsaines, entraînant un déséquilibre dans le corps et de nombreux problèmes de santé.
Types de stéatose hépatique
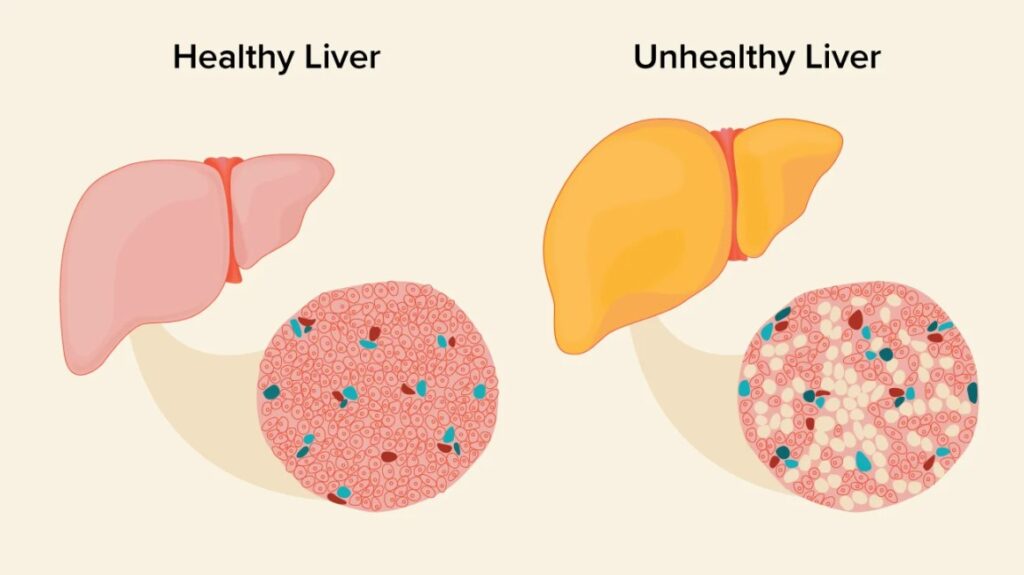
- Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD)
- Cause: Not related to excessive alcohol consumption.
- Effects: Causes inflammation and damage to liver cells.
- Progression: Does not typically worsen over time without additional contributing factors.
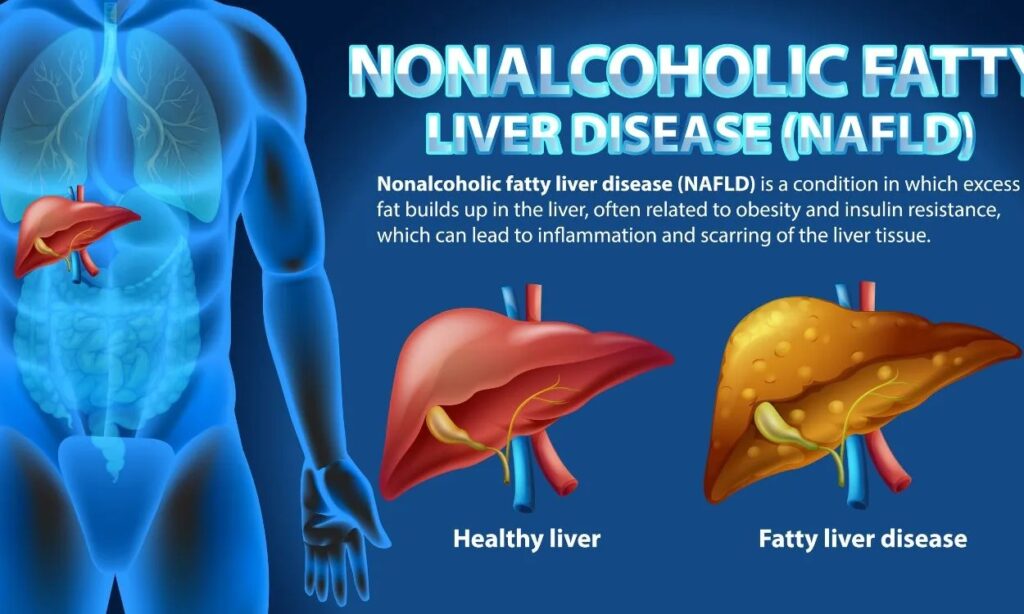
- Alcohol-Related Fatty Liver Disease (ARFLD)
- Cause: Directly related to excessive alcohol consumption.
- Effects: Can cause serious liver damage, including an enlarged liver.
- Symptoms: Early signs include pain and discomfort in the upper right side of the abdomen.
- Progression: Can improve with cessation of alcohol consumption; continued drinking can exacerbate the condition.
Symptômes et effets sur le corps
- Abdomen
- Fluid Retention: Water retention in the abdomen, caused by pressure in the liver’s blood vessels due to inflammation, leading to swelling and pain.
- Foot
- Swelling: Persistent swelling in the feet can indicate liver disease, as fluid accumulates due to gravity. This swelling can also occur from normal activities, but when persistent, it should be checked by a healthcare provider.
- Legs and Ankles
- Swelling: The ankles, legs, and feet can swell due to liver disease. Enlarged veins put pressure on the kidneys, hindering their ability to filter and remove excess fluid from the body naturally.
- Chest
- Enlargement: Liver disease can cause enlargement of the chest walls due to hormonal imbalances. This condition can decrease sexual desire and increase the risk of infertility.

Comprendre ces symptômes et leurs liens potentiels avec les maladies du foie est crucial pour une détection et une prise en charge précoces. De bonnes habitudes alimentaires et éviter une consommation excessive d’alcool peuvent réduire considérablement le risque de développer une stéatose hépatique.