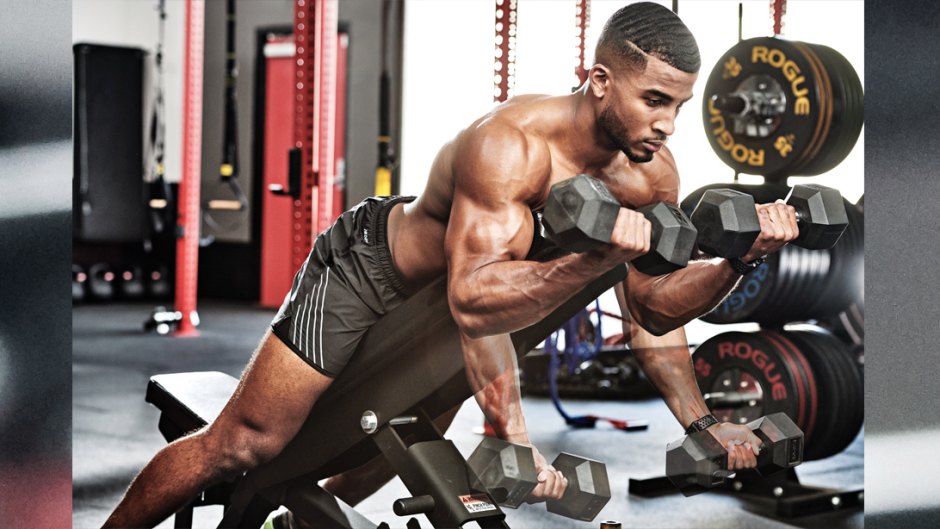
🏋️♂️ Understanding Muscular Hypertrophy
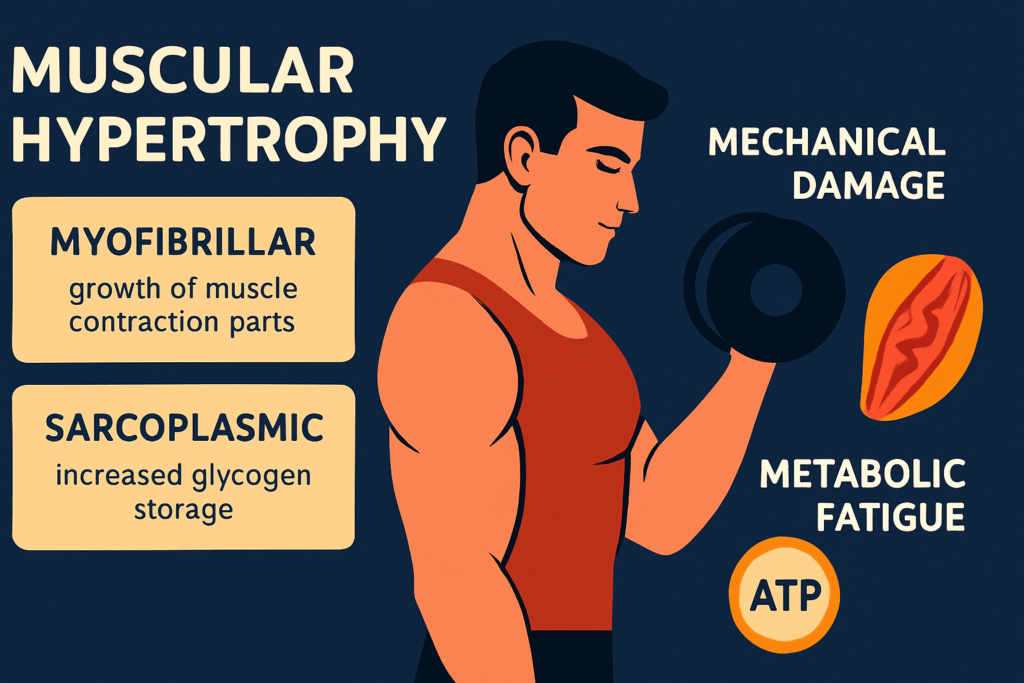
Muscular hypertrophy refers to the increase in the size of muscle cells, usually achieved through resistance training. If your goal is to tone your body, improve muscle definition, or build strength, hypertrophy should be part of your training plan.
💪 Types of Muscular Hypertrophy
There are two main types of muscular hypertrophy:
- Myofibrillar hypertrophy: Increases the size and strength of muscle fibers (contractile parts). Best for improving strength and speed.
- Sarcoplasmic hypertrophy: Increases energy storage (glycogen) in muscles. Ideal for endurance and muscle fullness.
| Type | Benefits | Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Myofibrillar | Strength, power, speed | Muscle fiber growth |
| Sarcoplasmic | Endurance, energy storage | Glycogen buildup in muscles |
Which type to train for?
It depends on your fitness goals. Powerlifters may focus more on myofibrillar, while bodybuilders or endurance athletes might aim for sarcoplasmic.
🧠 How Muscle Growth Happens
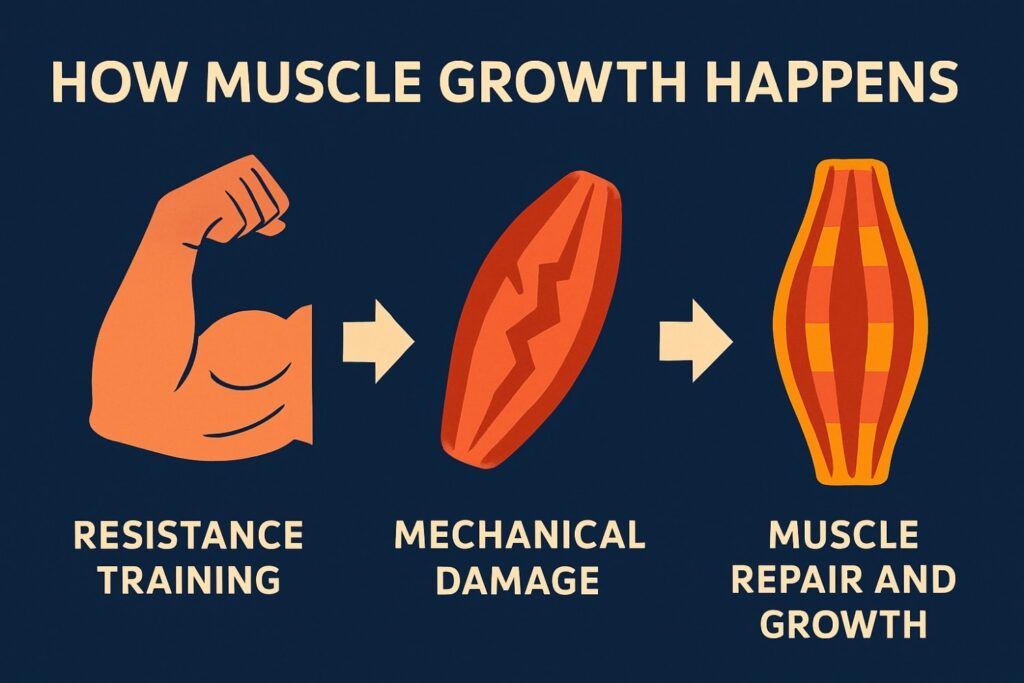
Muscle growth requires two key triggers:
1. Mechanical Damage
When you lift heavy weights, your muscle fibers experience micro-tears. The body repairs these tears, making the muscles bigger and stronger.
2. Metabolic Fatigue
Occurs when your muscles run out of energy (ATP) during training. This stress also stimulates growth.
🔑 Tip: You don’t always need to train to failure, but applying enough tension and stress to muscles is key for growth.
🏃♀️ Concentric vs. Eccentric Movements
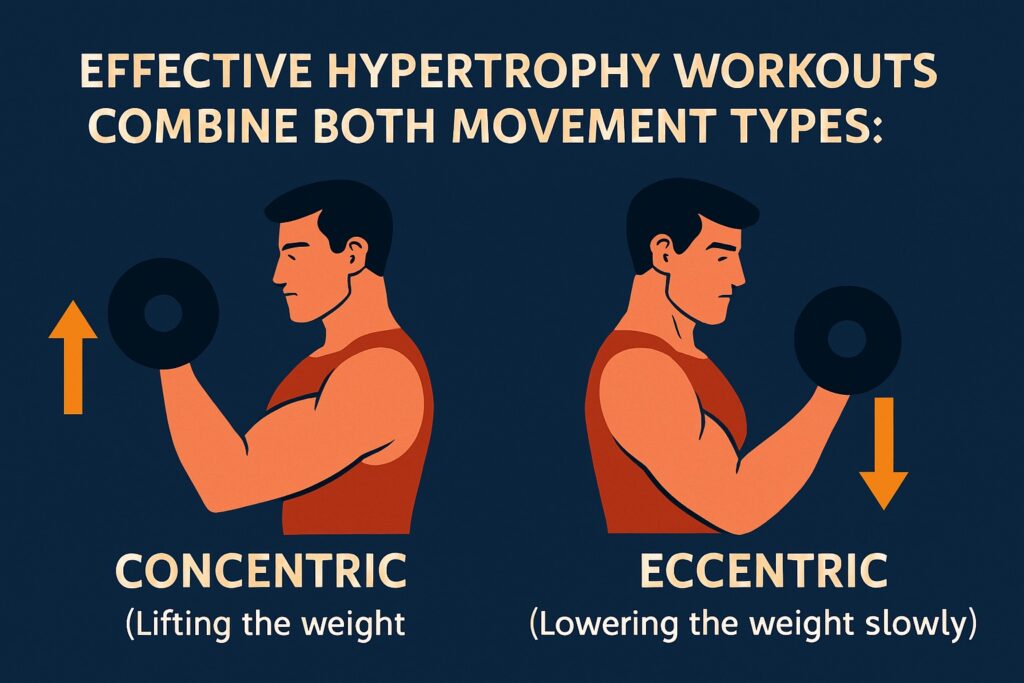
Effective hypertrophy workouts combine both movement types:
- Concentric: Lifting the weight (e.g., curling up a dumbbell).
- Eccentric: Lowering the weight slowly (e.g., returning to start position).
Best tempo for muscle growth:
- Lift (concentric) in 1–3 seconds
- Lower (eccentric) in 2–4 seconds
📅 How Often Should You Train?
Your workout frequency depends on your fitness level and goals:
- 3 days/week (full body or split): Ideal for most people.
- 2 days/week: Good for beginners or maintenance.
- Split routine: Alternate upper and lower body days to allow recovery.
Recovery is key.
Muscles grow when you rest — not during the workout.
✅ Pro Tips to Maximize Hypertrophy
- 🔁 Follow a reps-and-rest cycle:
Aim for 6–12 reps per set with 60–90 seconds rest. - 🏋️♂️ Lift challenging weights:
Use enough resistance to feel fatigue by the last rep. - 🔀 Change it up:
Rotate exercises to activate different muscle fibers. - 👨🏫 Work with a certified trainer:
For personalized programming and faster results. - 📈 Progress slowly:
Increase weight or intensity weekly to avoid plateaus or injury.
🧬 Myostatin-Related Muscular Hypertrophy (Rare Condition)
Some people have a rare genetic condition called myostatin-related muscular hypertrophy, caused by mutations in the MSTN gene.
- Results in low body fat and increased muscle mass
- It’s not harmful and doesn’t usually cause medical issues
- Can be diagnosed with genetic testing
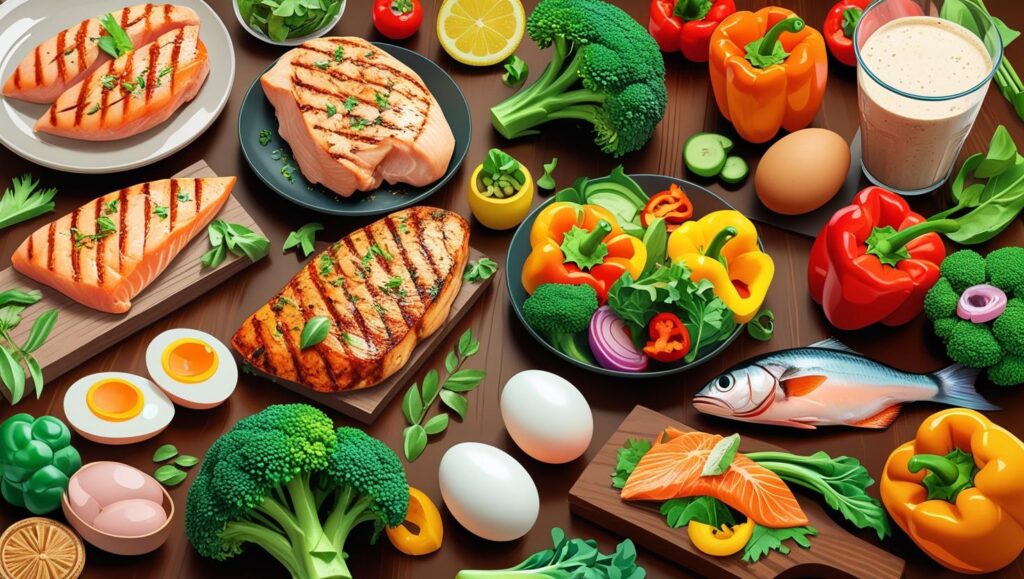
🥗 Nutrition for Muscle Growth

Muscle growth doesn’t just happen in the gym — it also happens in the kitchen.
- Consume protein-rich foods:
Lean meats, fish, eggs, or plant-based protein - Post-workout nutrition:
Eat or drink protein within 30 minutes after training to support recovery

⚠️ Before You Start
Always consult a healthcare provider before starting a new weightlifting program, especially if you have any health concerns or are new to resistance training.
🧠 Final Takeaway
Building muscle takes consistency, proper training techniques, enough recovery, and a supportive diet. Focus on progressive overload, challenge your muscles regularly, and fuel your body right — and you’ll see results over time.