The internet is rife with advice about how you can speed up metabolism. As you get older, though, it’s quite natural for various body systems to begin slowing down, including your metabolism. Unfortunately, this can result in weight gain and excess fat, which none of us want!
There are also thousands of weight-loss supplements and formulas that claim to get your body burning fat faster. The truth is, there is no “magic pill” that can change your body’s ability to burn fat. Much of it comes down to your own efforts in terms of diet, exercise, and self-care.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
- What Is Metabolism?
- What Happens If You Speed Up Metabolism?
- 6 Foods That Can Speed Up Metabolism
- Bottom Line
- More On Metabolism
What Is Metabolism?
Your metabolism is simply the process by which your body converts food into energy. This is a complex biochemical process in which the calories in food and beverages combine with oxygen to release the energy that you need to carry out various activities.
Your body requires energy all the time, even when you’re resting. Dozens of different functions are going on within you that you don’t even think about, such as breathing, circulating blood, modulating hormones, restoring, and repairing cells.
Similarly, your body requires a certain number of calories to carry out these basic functions. This is known as your basal metabolic rate or metabolism.
Several factors determine the speed of your metabolic rate, including:
- Your body size and composition – People with more muscle burn more calories, even at rest.
- Your gender – Men generally have less body fat and more muscles than women, so they burn more calories.
- Your age – As you get older, your body’s muscle content tends to decrease and fat begins to increase, which can slow down your metabolism.
What Happens If You Speed Up Metabolism?
When your metabolism is functioning at its best, you’ll experience lots of health benefits. It’s important to remember that many factors are involved in your metabolic rate, and weight is only one of them!
Having a fast metabolism will mean that your energy levels are much more stable, and you hardly feel tired. This is because your body will be efficiently converting the food you eat into fuel, providing you with a steady source of energy.
People with great metabolisms can also stay mentally focused. You are less likely to gain weight and can shed pounds quickly when you need to.
6 Foods That Can Speed Up Metabolism
It might seem counter-intuitive to think that certain foods could speed up metabolism, but it’s true. Your body needs some nutrients to kick-start your fat-burning processes; that’s why skipping meals may not actually help you lose weight in the long run.
The following foods have been shown to help boost your metabolism and get your weight-loss journey on track:
What If You Can Get in Shape at Home?
1. Lean Meats

It takes a lot more work to digest protein than it does to digest carbohydrates or fat. Because of that, experts recommend eating fresh, lean meats such as poultry and fish.[1] The digestion process requires a lot of energy, so you’re burning calories in order to break them down. Studies have shown that protein can increase your post-meal calorie burn by as much as 35%.[2]
What’s more, protein is required for building muscle mass. The more muscle you have, the faster your metabolism. Hence, aim to include some protein in every meal and snack throughout the day.
2. Legumes
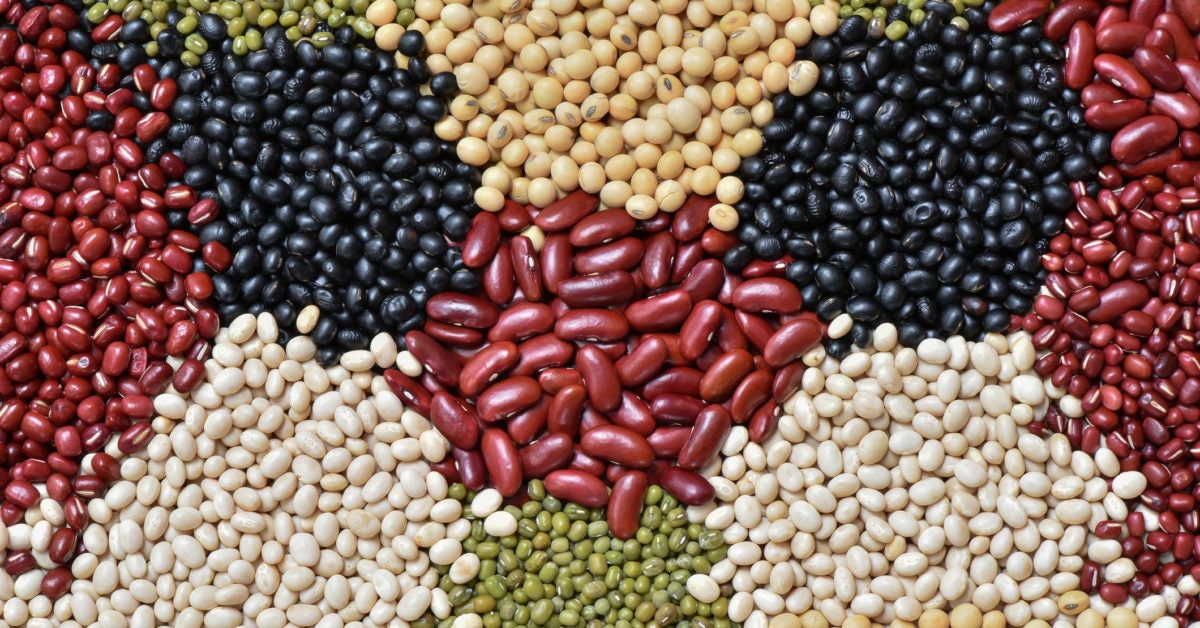

Beans and pulses are an excellent source of plant-based protein. They’re also rich in fiber, both soluble and insoluble. Your body uses up a lot of energy when it breaks down the fiber and protein, and that keeps your metabolism in good working order.
The high fiber content of beans also helps to keep your blood sugar levels steady and prevent those mid-afternoon sugar cravings.[3]
Furthermore, legumes provide iron, zinc, and selenium. These are minerals that your thyroid needs to produce sufficient amounts of hormones. Without them, your metabolism can slow down or become impaired.
3. Nuts
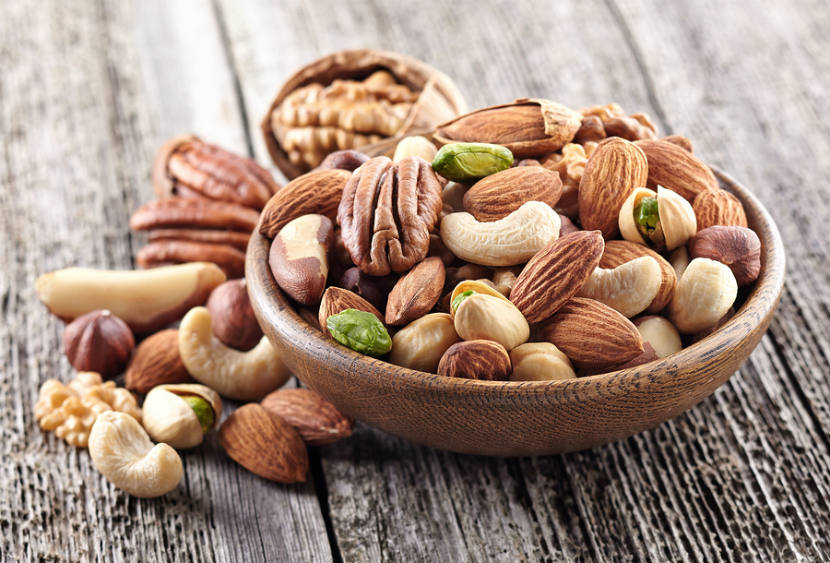

Nuts are another great source of protein and fiber. Research has shown that people who eat nuts regularly tend to have a lower risk of insulin resistance and smaller waist sizes than those who don’t eat them.[4] When you have lower insulin resistance, your body is less likely to store fat or develop type 2 diabetes. Again, nuts take longer to break down, which makes them more satisfying and better for your metabolism.
Most importantly, research has even found that nuts can ramp up your metabolism. Several trials have noted that nuts provide increased energy expenditure that may help you burn an extra 10% of your overall energy yield.[5]
4. Whole Grains
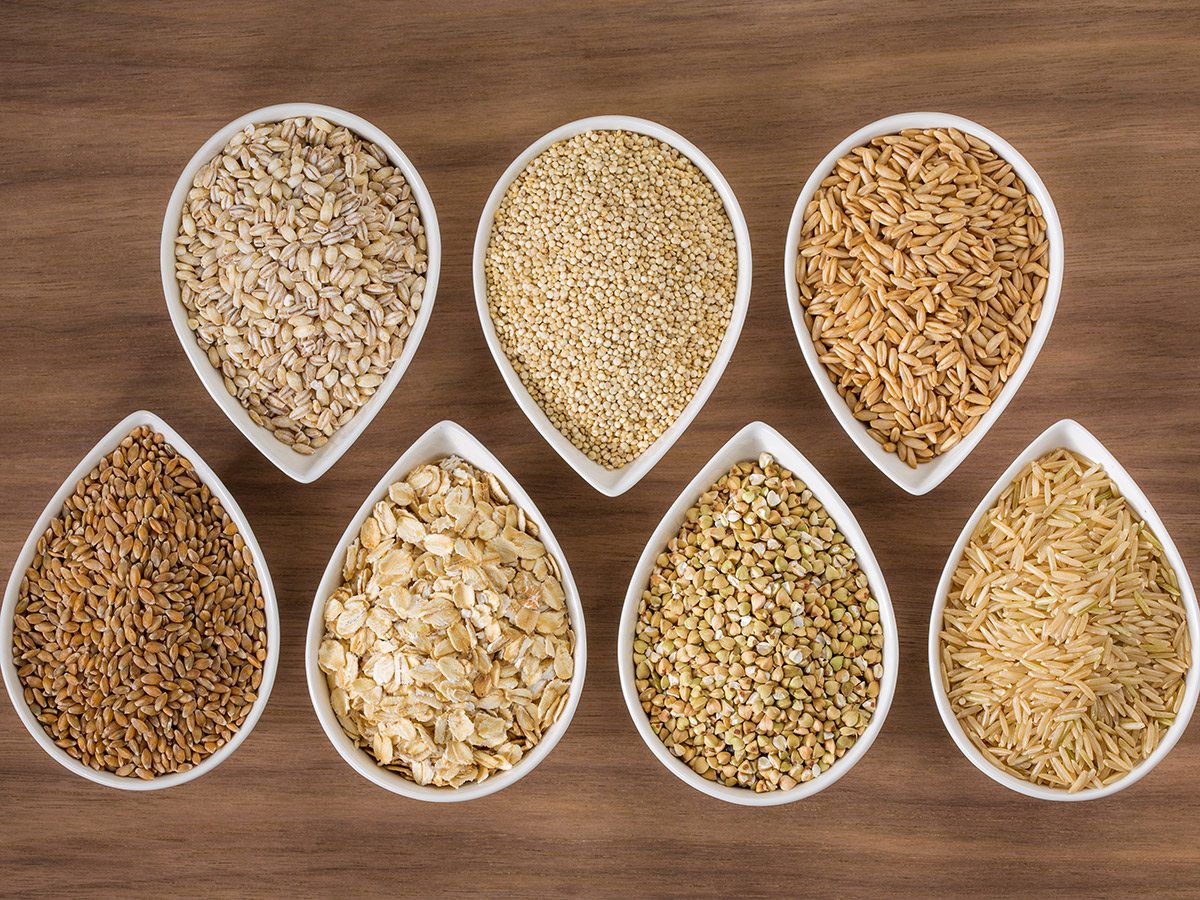

Whole grains are a complex carbohydrate that consists of a longer series of sugars. It entails that your body takes longer to break them down, so your metabolism is burning steadily for a longer period. Researchers have found that consuming whole grains increases your post-meal energy expenditure by up to 50% more than eating processed foods.[6]
Foods with complex carbohydrates typically have more nutrients, particularly B vitamins. They play a major part in converting the food you eat into energy, which is the essence of your metabolic function. Specifically, vitamin B12 is often associated with weight loss because it boosts metabolism and provides long-lasting energy.
5. Probiotic Foods
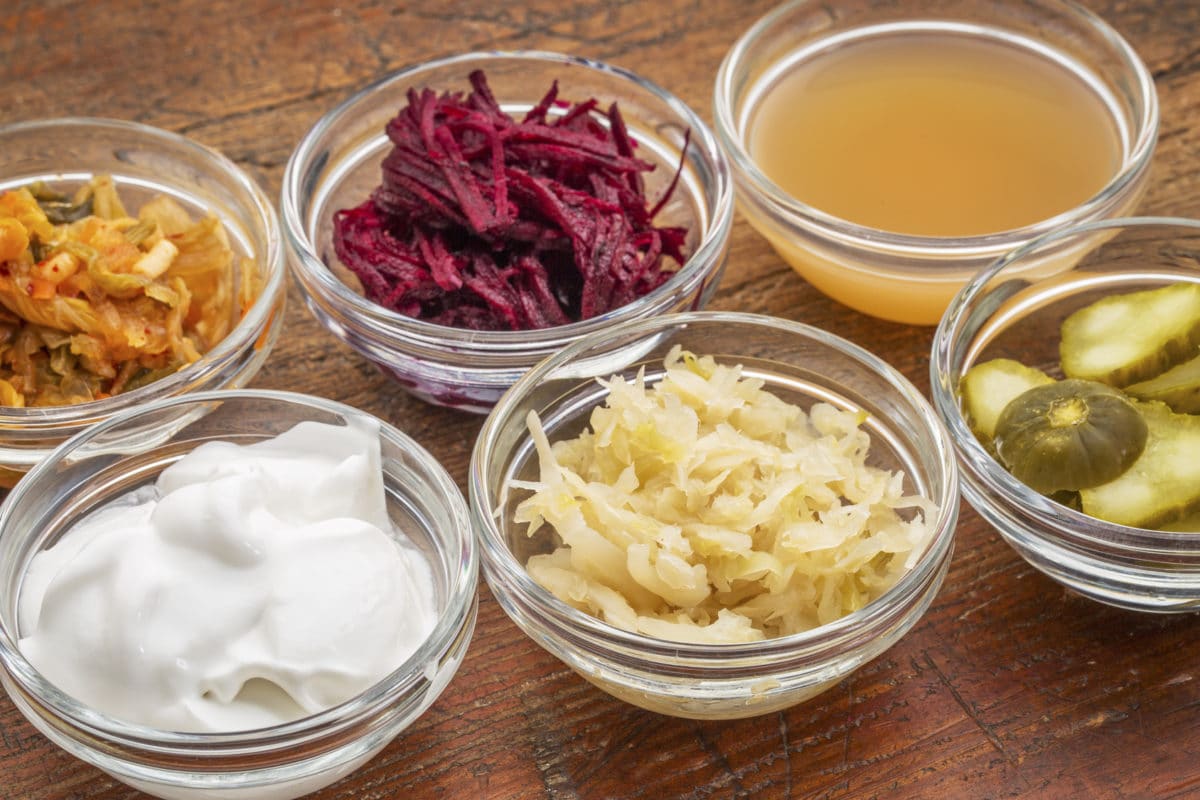

Fermented foods such as yogurt, kefir, kimchi, and sauerkraut help to increase the number of good bacteria in your gut. These bacteria are largely responsible for digesting food in your intestines and facilitating the uptake of nutrients.
A 2012 study published in the Journal of Functional Foods reported that when adults ate about 1/2 cup of probiotic yogurt at dinner every night for six weeks, they lost 3-4% body fat. This compared with adults who ate plain yogurt and only lost 1% body fat.
It’s been suggested that probiotics change the way the body metabolizes bile acids. These acids are made by the liver and their primary function is to break down fats in the upper gut. If probiotics can influence how bile acids are metabolized, they may change how much fat your body can absorb from food.
6. Caffeine

Caffeine is a powerful stimulant known for helping you to “wake up” and boosting your metabolism. It works by blocking a neurotransmitter called adenosine, which causes other neurotransmitters to release more dopamine and norepinephrine.
This helps you feel more alert and energized, which in turn can allow you to exercise longer. Remember, however, that drinking too much caffeine can also trigger a chronic stress response and leave you feeling burnt out, so you should take it in small doses.
Studies have shown that caffeine can increase your resting metabolic rate by around 3–11%, depending on the size of your dose.[10] It’s also shown that this can help burn fat faster. One study even showed that people who took caffeine-based supplements experienced increased fat burning by as much as 29%. Thus, it has led researchers to suggest that caffeine can significantly influence energy balance and speed up metabolism.
Bottom Line
Remember, whilte this article focuses on what to eat, to really speed up your metabolism and burn fat, you need to make efforts in terms of exercise and self-care too. Start eating healthy with the above foods that I suggested, and exercise regularly to keep yourself moving.