Introduction
Gut health encompasses the effective functioning and overall condition of your gastrointestinal system, from the esophagus to the lower intestines. It involves a complex community of microorganisms known as the gut microbiome, crucial for digesting food into essential nutrients.
The Gut Microbiome: A Delicate Balance

The gut microbiome consists of diverse microorganisms including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa. Its composition is influenced by diet, physical activity, medications, and genetics, impacting various aspects of health.
Impact on Health
Gut microbes play roles in immune function, metabolism, and neurological processes. They produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) vital for colon cell energy and immune support. Imbalances can lead to obesity, metabolic issues, and autoimmune diseases.
The Gut-Brain Connection
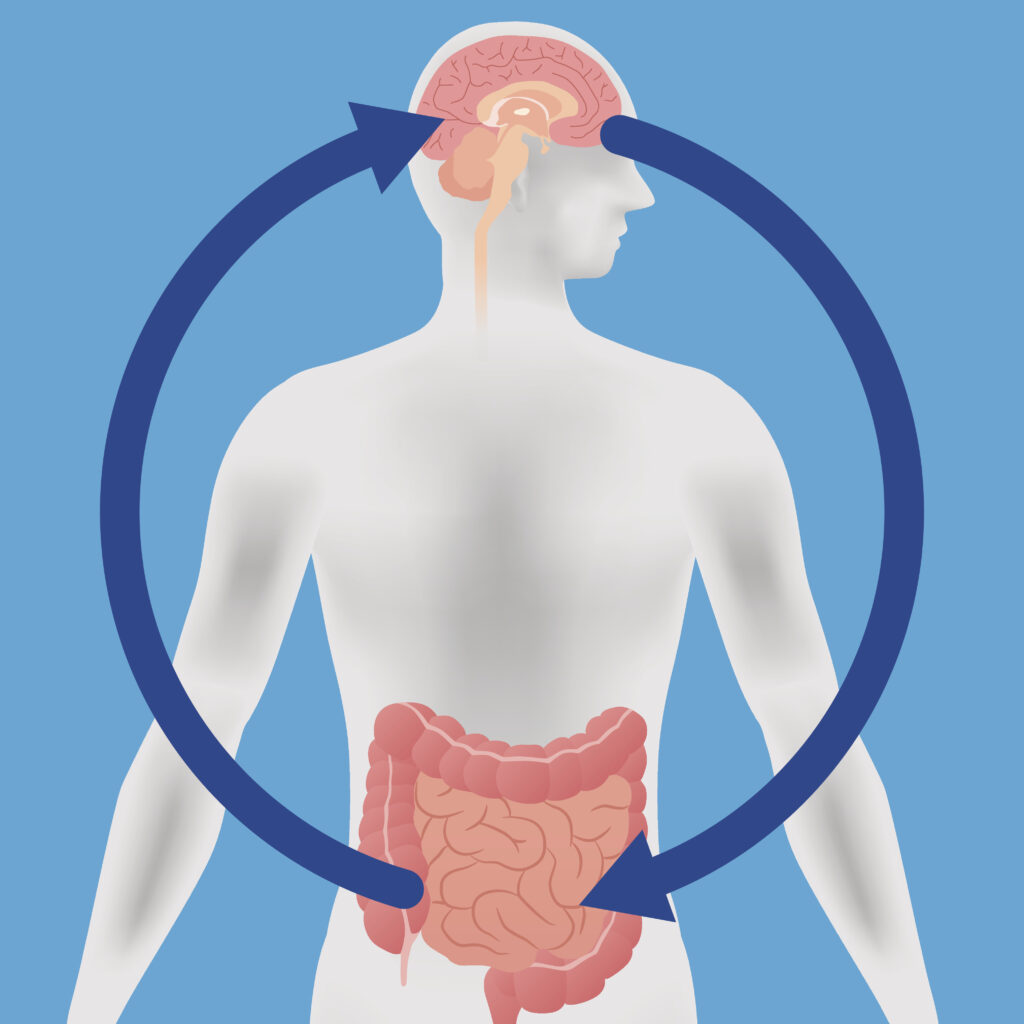
Often termed the “second brain,” the gut houses millions of neurons and produces neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine. This gut-brain axis influences mood, appetite, and overall well-being through bidirectional communication with the central nervous system.
Why Gut Health Matters

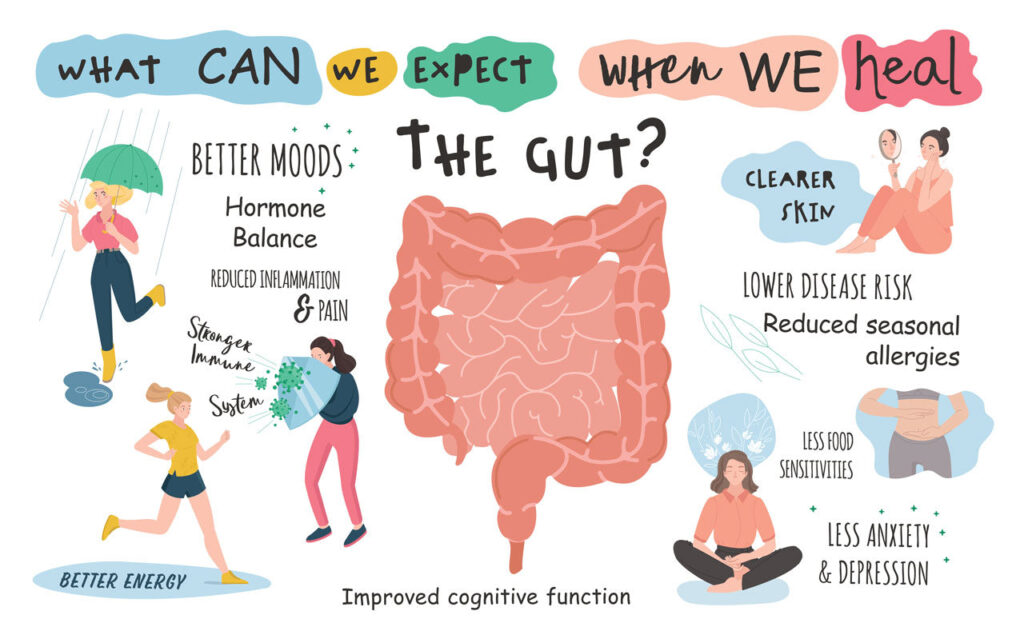
- Immune System: A healthy gut supports immune function, distinguishing between harmful and harmless substances, reducing autoimmune risks.
- Mental Health: Gut imbalances affect neurotransmitter production, impacting mood and cognitive function, potentially contributing to anxiety and depression.
- Chronic Diseases: Disruptions in gut health correlate with conditions like type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and gastrointestinal disorders.
- Digestive Function: Optimal nutrient absorption and digestion depend on a balanced gut microbiome, crucial for overall physical health.
Factors Contributing to Good Gut Health

Maintaining a diverse microbiota, supporting gut barrier integrity, promoting efficient digestion, and managing lifestyle factors like diet and stress are vital for gut health.
Causes of Poor Gut Health
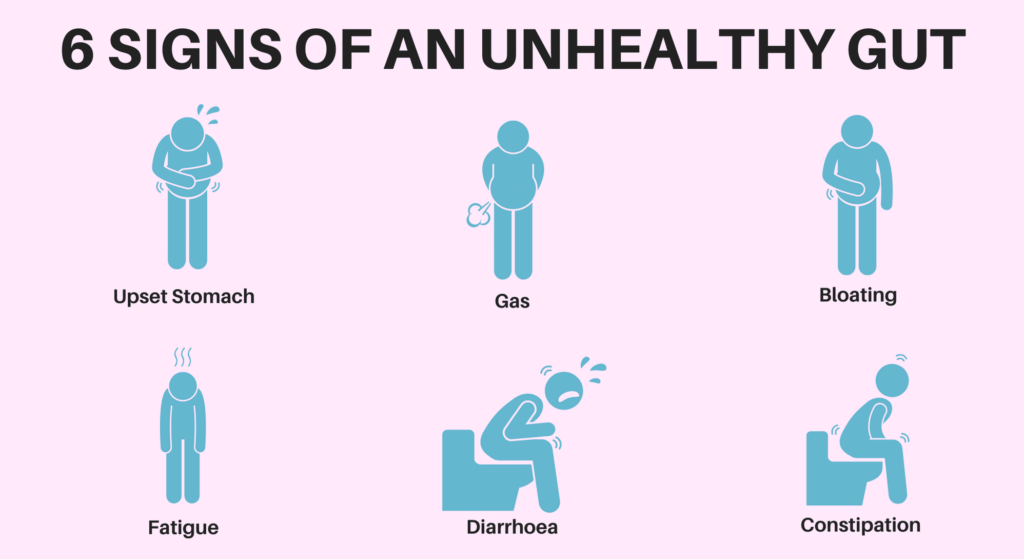
Poor diet choices, medications (especially antibiotics), and lifestyle factors like stress can disrupt gut microbiota balance, leading to digestive discomfort and health complications.
Signs and Solutions for Gut Health
Recognizing symptoms of a healthy or unhealthy gut, addressing issues through dietary adjustments, lifestyle modifications, and possibly medical consultation ensure optimal gut health and overall well-being.
Gut Health Foods

Incorporating high-fiber foods, probiotics, prebiotics, and anti-inflammatory foods into your diet supports a balanced gut microbiome and enhances overall health.
Conclusion
Maintaining gut health is essential for digestive efficiency, immune resilience, and mental well-being. By nurturing a diverse gut microbiome through balanced nutrition and lifestyle habits, you can support your overall health and vitality.